What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Artificial Intelligence, or AI, is like giving computers a brain to think and learn, similar to how humans do. It’s a way to make machines smart enough to solve problems, make decisions, and perform tasks that usually require human intelligence.
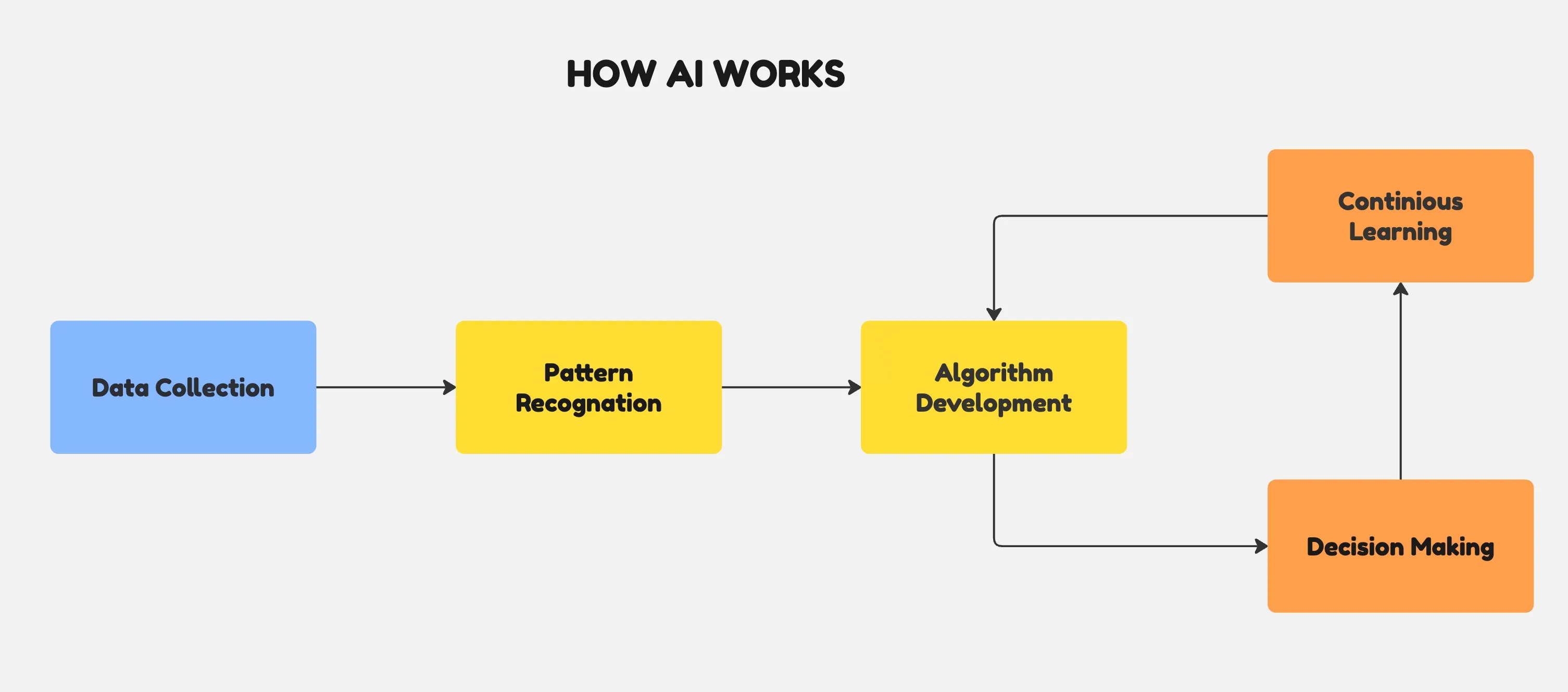
How AI Works
-
Data Collection: AI systems are fed large amounts of relevant data.
-
Pattern Recognition: The AI analyzes this data to identify patterns and trends.
-
Algorithm Development: Based on the patterns, algorithms are developed or refined.
-
Decision Making: Using these algorithms, the AI makes decisions or predictions when presented with new information.
-
Continuous Learning: The AI improves its performance over time through more data and feedback, a process known as machine learning.
Core Concepts of AI
1. Machine Learning
At the heart of AI is machine learning, which allows systems to learn and improve from experience without being explicitly programmed. It’s like teaching a computer to learn on its own.
2. Neural Networks
Inspired by the human brain, neural networks are a set of algorithms designed to recognize patterns. They interpret sensory data through a kind of machine perception, labeling or clustering raw input.
3. Deep Learning
A subset of machine learning, deep learning uses multi-layered neural networks to analyze various factors with a structure similar to the human neural system.
4. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP focuses on the interaction between computers and human language, enabling machines to read, understand, and derive meaning from human languages.
5. Computer Vision
This field deals with how computers gain high-level understanding from digital images or videos, aiming to automate tasks that the human visual system can do.
Types of AI
AI can be categorized into different types based on their capabilities and scope:
-
Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI):
- Designed to perform specific tasks
- Examples: virtual assistants, image recognition systems
- This is the type of AI we currently have and use in everyday applications
-
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI):
- Systems that can perform any intellectual task that a human can do
- Possesses the ability to transfer knowledge between domains
- Currently theoretical and not yet achieved
-
Artificial Super Intelligence (ASI):
- AI that surpasses human intelligence and ability across all domains
- Hypothetical scenario where AI becomes smarter than the best human brains in practically every field
- Currently exists only in theory and science fiction
AI Approaches and Techniques
While the previous categories describe the scope of AI systems, there are various approaches and techniques used in AI development. Here are some significant approaches:
1. Supervised Learning
- AI learns from labeled training data
- Requires human intervention to provide the correct labels
- Examples: Image classification, spam detection
2. Unsupervised Learning
- AI finds patterns in unlabeled data
- Discovers hidden structures in data without human guidance
- Examples: Customer segmentation, anomaly detection
3. Reinforcement Learning
- AI learns through interaction with an environment
- Receives rewards or penalties for actions
- Examples: Game playing AI, robotics control
4. Generative AI
- Focuses on creating new content rather than just analyzing existing data
- Can create text, images, music, and video
- Uses techniques like GANs and transformers
- Examples: GPT models, DALL-E, Midjourney
5. Expert Systems
- Rule-based systems that emulate the decision-making ability of a human expert
- Uses predefined rules and knowledge base
- Examples: Medical diagnosis systems, financial planning tools
6. Evolutionary Computation
- Inspired by biological evolution
- Uses mechanisms like mutation, selection, and reproduction
- Examples: Optimizing complex systems, solving scheduling problems
7. Fuzzy Logic
- Deals with reasoning based on “degrees of truth” rather than boolean logic
- Useful for handling uncertainty and imprecision
- Examples: Control systems, decision support systems
8. Computer Vision
- Focuses on how computers can gain high-level understanding from digital images or videos
- Includes tasks like image recognition, object detection, and scene reconstruction
- Examples: Facial recognition, autonomous vehicles
9. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- Deals with the interaction between computers and human language
- Includes tasks like language translation, sentiment analysis, and text summarization
- Examples: Chatbots, language translation services
Each of these approaches has its strengths and is suited for different types of problems. Many modern AI systems combine multiple approaches to achieve more sophisticated and capable artificial intelligence.
The Impact of AI
AI is transforming various sectors, including:
- Healthcare: Assisting in diagnosis and treatment planning
- Finance: Detecting fraudulent transactions and providing investment advice
- Education: Personalizing learning experiences
- Transportation: Enabling autonomous vehicles and optimizing traffic flow
- Manufacturing: Enhancing production efficiency and quality control
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While AI offers immense potential, it also presents challenges:
- Data privacy and security
- Potential job displacement
- Ethical decision-making in AI systems
- Ensuring AI benefits all of humanity
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence, from narrow AI to the theoretical realms of AGI and ASI, is reshaping our world. As we progress from current AI technologies towards more advanced systems like Generative AI, the potential for innovation grows, as do the ethical considerations we must address. Understanding these concepts is crucial as AI continues to evolve and integrate into various aspects of our lives and industries.